 Time:2021-08-18
Time:2021-08-18
Carbon neutrality, plastic reduction, green ...... These concepts have become a consensus in society. Manufacturing companies are in action, exploring the possibilities on the path of sustainable development. 3D printing, which has played an active role in lowering energy consumption and reducing carbon emission has risen to prominence.

What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also referred to as additive manufacturing, is an advanced manufacturing technology originated in the 1980s that integrates computers, machinery, CNC and materials.
Compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing (e.g. cutting) and equivalent manufacturing (e.g. forging), this mode of production barely has any material waste, resulting in both cost savings and environmental benefits. It can even localize the production and reduce transportation. After paying for the ‘drawings’, customers are able to print the required products locally, thus reducing the need of line-haul and the greenhouse gas emission that comes with it.
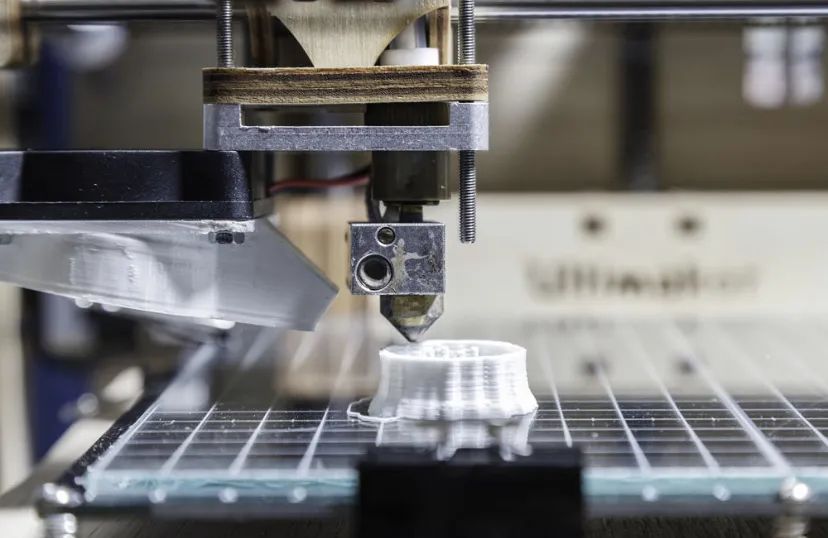

Limitations of Traditional Printing Materials
At present, 3D printing mainly uses resin and plastics as the materials. The most rapidly developing plastic material, polypropylene (PP), has great potential for application in the field of 3D printing due to its low density, high strength, good heat resistance and insulation, chemical stability and low price.

However, the process of melt crystallization causes great shrinkage in PP, which makes it prone to warping and deformation during 3D printing. The final product may therefore be less accurate than desired. In addition, the printed product is of low toughness and high loss, often ending up of having no actual use.
New Materials Driving the Development of 3D Printing Technology
NHU’s new material research team has dived headfirst into the emerging field of 3D printing since 2019 and has successfully developed polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), boosting the development of 3D printing technologies.
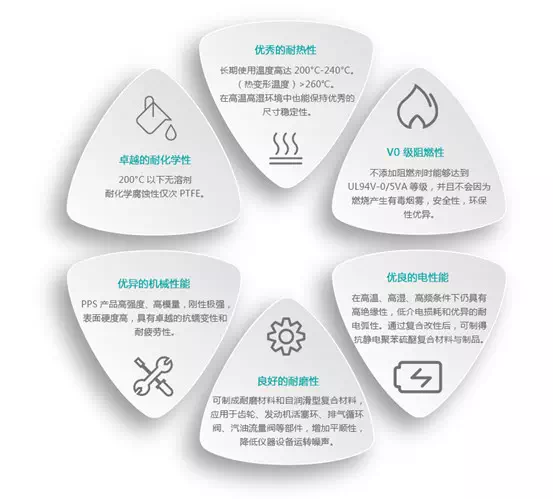
PPS is a thermoplastic material with excellent performance in heat resistance, chemical resistance, flame retardancy and electrical properties. It has a heat deflection temperature of 260°C and a long-term service temperature of over 200°C. In addition, its chemical resistance is second only to fluorine resins, and it has a V-0 flame rating. When ground into powder, it has high fluidity; when spread out,the powder bed is leveled and smooth, resulting in high accuracy for 3D printing.
According to the R & D staff, the particle size of the material has been one of the key factors affecting the structure and performance of 3D printed parts. PPS micro powder effectively addresses the limitations of the particle size of the material, promoting its application in 3D printing. With excellent thermal stability, PPS micro powder can be recycled multiple times, greatly reducing the cost of printing. This backs up the argument of the pollution-free benefit of 3D printing.
The new PPS material developed by NHU has been widely used for areas of low-carbon emission and environmental protection. For example, PPS filter-bag made of PPS resin has been installed in dust collectors in domestic coal-fired power plants, reducing the smoke emissions of the plants; NEV parts made of PPS materials reduce the weight of the vehicle and its battery and increase the mileage and energy utilization, contributing to sustain

As a new year unfolds, NHU has begun on a high note, receiving a series of honors that signal a strong start and lay a solid foundation for the year ahead.
View details

NHU’s project, “Development and Industrialization of Integrated Manufacturing Technologies for High-Quality Solid Methionine” was awarded the First Prize of the Science and Technology Progress Award in recognition of its significant technological breakthroughs and industrial value.
View details

On December 12, the forum “Resilience, Symbiosis, Leadership – Release of the Top 100 Chinese Multinational Private Enterprises and the Zhejiang Business Think Tank Dialogue on the 15th Five-Year Plan” was successfully held in Hangzhou. At the event, the Center For Chinese Multinationals (CCM) of Zhejiang University Business School (ZIBS) released the Top 100 Chinese Multinational Private Enterprises 2025 list. NHU was honored to be included, in recognition of its forward-looking global strategy, robust and continuously innovative R&D system, and growing international influence.
View details